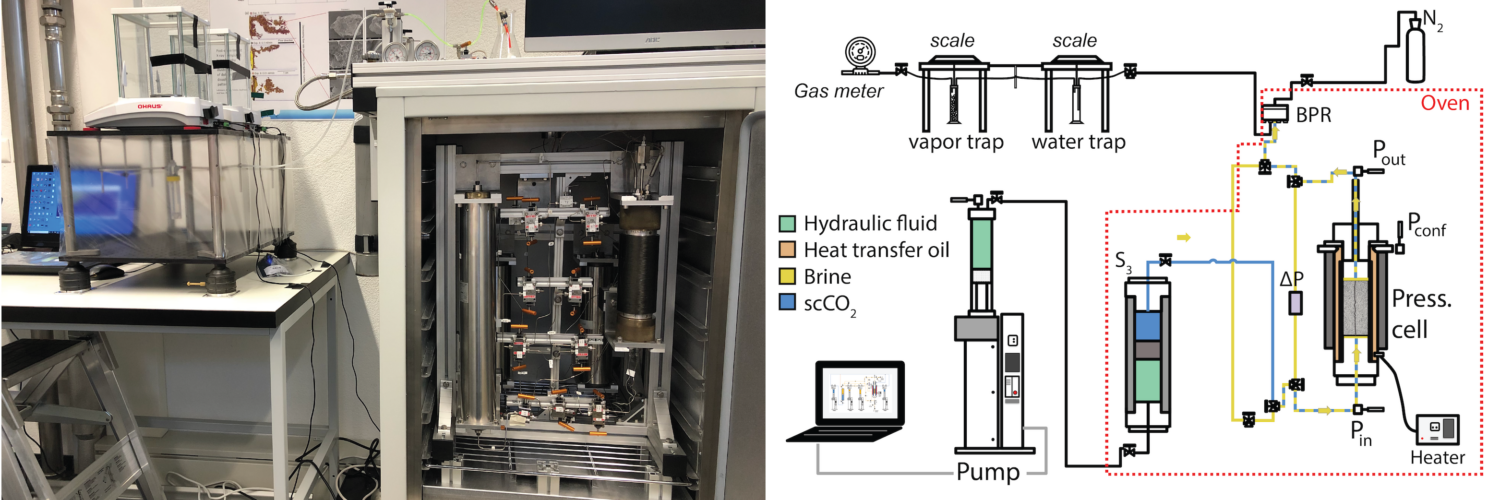
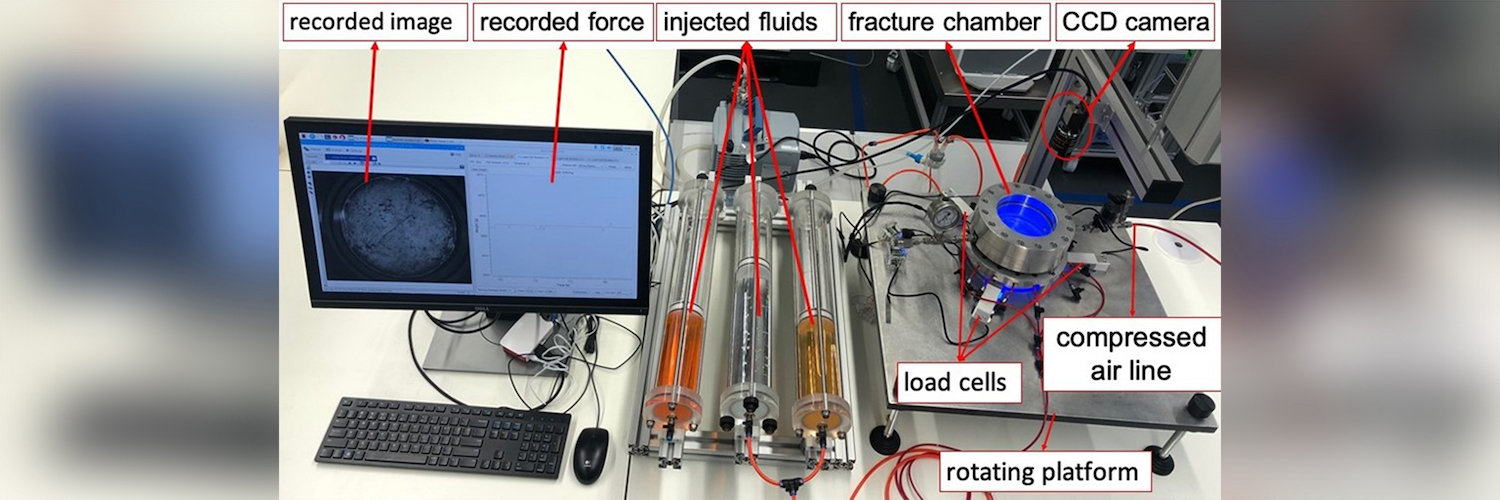
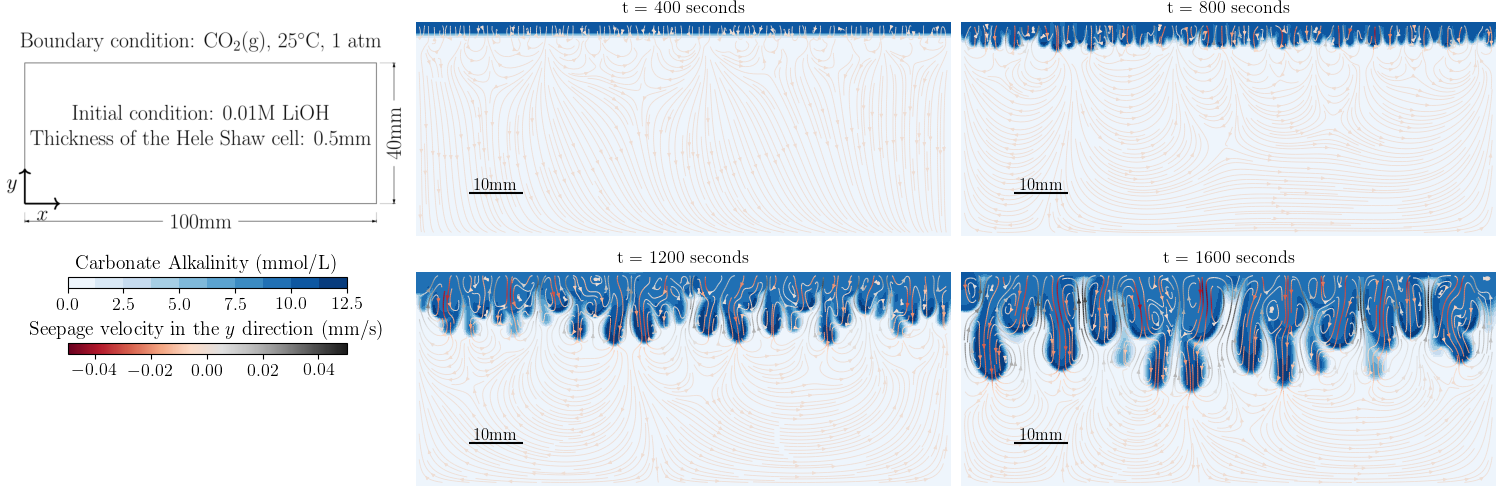
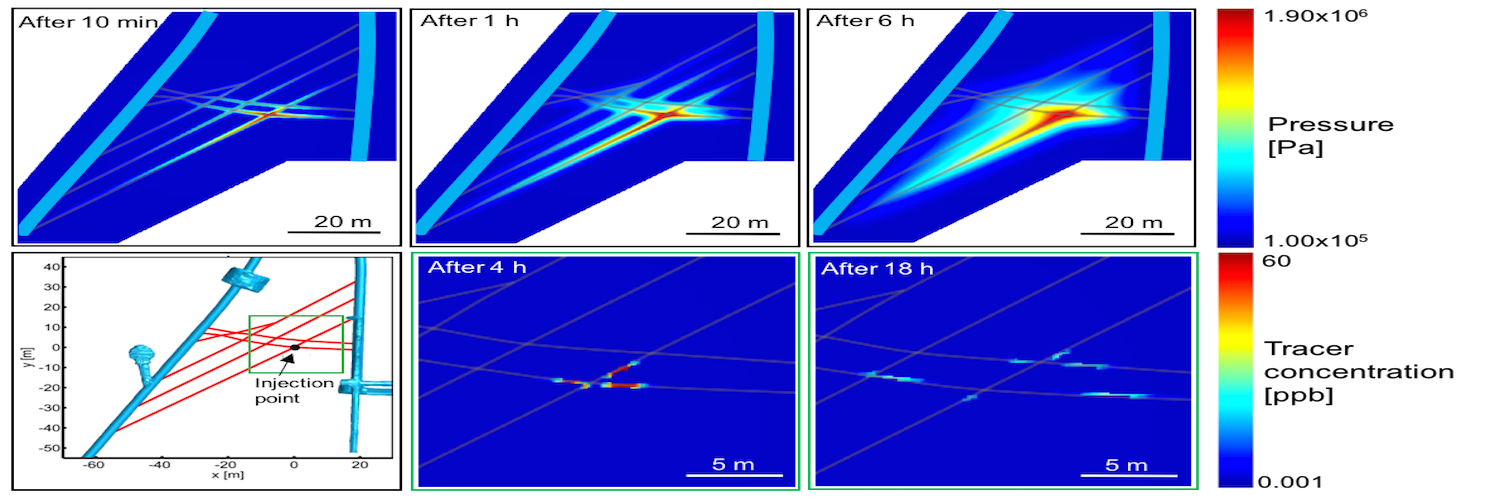
Mission Statement
The Geothermal Energy & Geofluids group is endowed by the Werner Siemens Foundation and investigates reactive fluid (water, CO2, CxHy, N2) and (geothermal) energy (heat, pressure) transfer in the Earth’s crust employing computer simulations, laboratory experiments and field analyses to gain fundamental insights and to address a wide range of societal goals and concerns. ➞ Read More
GEG News
Geothermal energy has great potential, but drilling is expensive. That is why intensive research is being conducted into affordable drilling technologies. One such method is Directional Steel Shot Drilling (DSSD). A research team at ETH Zurich, together with international partners, has investigated this still-developing technology and assessed its potential for Switzerland. Special report: https://pubdb.bfe.admin.ch/en/publication/download/12285
18.08.2025
NEW Open Position
06.05.2024
Doctoral Examination Mohamed Ezzat
On May 6, 2024, Mohamed Ezzat has successfully defended his PhD thesis, entitled: “Numerical and Experimental Investigation of the Plasma-Pulse Geo-Drilling Technology“.
A GEG paper receives the Rock Mechanics Bulletin Excellent Paper 2022-2023 Award. The paper is:
Li, Z., X. Ma, X.-Z. Kong, M.O. Saar, and D. Vogler, Permeability evolution during pressure-controlled shear slip in saw-cut and natural granite fractures, Rock Mechanics Bulletin, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rockmb.2022.100027 [Download] [View Abstract]Fluid injection into rock masses is involved during various subsurface engineering applications. However, elevated fluid pressure, induced by injection, can trigger shear slip(s) of pre-existing natural fractures, resulting in changes of the rock mass permeability and thus injectivity. However, the mechanism of slip-induced permeability variation, particularly when subjected to multiple slips, is still not fully understood. In this study, we performed laboratory experiments to investigate the fracture permeability evolution induced by shear slip in both saw-cut and natural fractures with rough surfaces. Our experiments show that compared to saw-cut fractures, natural fractures show much small effective stress when the slips induced by triggering fluid pressures, likely due to the much rougher surface of the natural fractures. For natural fractures, we observed that a critical shear displacement value in the relationship between permeability and accumulative shear displacement: the permeability of natural fractures initially increases, followed by a permeability decrease after the accumulative shear displacement reaches a critical shear displacement value. For the saw-cut fractures, there is no consistent change in the measured permeability versus the accumulative shear displacement, but the first slip event often induces the largest shear displacement and associated permeability changes. The produced gouge material suggests that rock surface damage occurs during multiple slips, although, unfortunately, our experiments did not allow quantitatively continuous monitoring of fracture surface property changes. Thus, we attribute the slip-induced permeability evolution to the interplay between permeability reductions, due to damages of fracture asperities, and permeability enhancements, caused by shear dilation, depending on the scale of the shear displacement.
10.03.2023
Doctoral Examination Batmagnai Erdenechimeg

On March 3, 2023, Batmagnai Erdenechimeg has successfully defended his PhD thesis, entitled: “Magnetotelluric exploration of intermediate temperature geothermal systems and mineral resources in central Mongolia”.
December 2022, RWTH Aachen
Dr. Paromita Deb has been given the Dr. Karl-Heinrich Heitfeld Award for the best doctoral thesis in the Division of Earth Sciences and Geography.
Read more – link to RWTH Aachen
Dr. Paromita Deb has been given the Dr. Karl-Heinrich Heitfeld Award for the best doctoral thesis in the Division of Earth Sciences and Geography.
Read more – link to RWTH Aachen
On October 28, 2022, Isamu Naets has successfully defended his PhD thesis, entitled: “A pore scale investigation of fluid flow heterogeneity and solute transport in rough-walled fractures”.
The biggest geothermal event in Europe has ended. More than 1300 participants attended EGC2022. The next EGC2025 will be held in Zurich, from 6 to 10 October 2025, organized by Geothermie Schweiz and co-organized by ETH Zurich.
On September 16th, 2022, Po-Wei Huang has successfully defended his PhD thesis, entitled: “Reactive transport modeling at the pore scale and upscaling to the Darcy scale”.
GEG Events
NEXT EVENT
03.03.2026 14:00-15:00
t.b.a.Lily SUHERLINA (GEG group presentation)
GEG Meetings, ETH Zurich
Newest GEG Papers
Refereed journal papers accepted the last 6 months
Underlined names are links to current or past GEG members
CO2-Plume Geothermal (CPG) after enhanced oil recovery (EOR)
Küçük, S., R. Farajzadeh, M. Brehme, W.R. Rossen, and M.O. Saar, Geoenergy Science and Engineering, 257 Part B, 2026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoen.2025.214261 [Download] [View Abstract]The global energy transition requires novel carbon utilization methods to enable integrated and optimized low-carbon energy production. Coupling CO2-based geothermal energy extraction with CO2-enhanced oil recovery (EOR) represents a promising yet largely unexplored approach for improving resource efficiency and carbon sequestration. This study investigates the integration of CO2-Plume Geothermal (CPG) energy production with CO2-EOR in mature oil reservoirs using numerical simulations of conceptual heterogeneous reservoir models. The interplay between EOR and CPG performance in terms of energy production and CO2 storage is evaluated and compared to understand the geotechnical implications of this integration. The analysis highlights that initiating CPG operations after EOR significantly benefits from the established CO2 plume, facilitating immediate and efficient geothermal energy extraction. Results show that integrating CPG with EOR increases total energy recovery by 20%–50% relative to the energy produced by EOR alone, yielding CPG thermal power outputs ranging from 13 to 23 MWth/km2. Continued CO2 injection during CPG operations further increases total CO2 storage by 80%–280%, driven primarily by improved volumetric sweep of previously unswept reservoir volumes and enhanced CO2 density resulting from reservoir cooling. While reservoir heterogeneity strongly influences oil recovery during EOR, its effect on CPG thermal output is less pronounced, since native reservoir fluids (oil and brine) have already been largely displaced during the EOR stage, and the CO2 plume gradually stabilizes over time. These findings demonstrate the viability and advantages of integrated CO2-EOR and CPG systems, offering insights into novel methods essential for sustainable subsurface resource management and climate-change mitigation. (Paper accepted 2025-10-19) Natural Convection in Porous Media: The Role of Porosity and Conductivity Ratios in the Transition from Laminar to Inertial Convection
Schwendener, D., J. Noir, J. Latt, C. Coreixas, and X.-Z. Kong, Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2025. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2025.11014 [Download] [View Abstract]We study natural convection in porous media using a lattice Boltzmann method that recovers incompressible Navier--Stokes--Fourier dynamics. The porous structure consists of a staggered two-dimensional cylinder array with half-cylinders at the walls, forming a Darcy continuum at the domain scale. Hydrodynamic reference simulations reveal distinct flow regimes: laminar (Darcy), steady-inertial (Forchheimer), and vortex-shedding. We then analyse the effects of porosity and solid-to-fluid conductivity ratio ($k_s/k_f$) on natural convection. At low porosity ($\varphi = 33\%$), convection is highly sensitive to thermal coupling, particularly for insulating solids, whereas conductive matrices buffer this effect through lateral diffusion. Increasing porosity ($\varphi = 43\%$) smooths the transition as solid and fluid phases become more balanced. Across the explored range, two inertial regimes emerge governed by plume-scale confinement. The transition from Darcy to inertia-driven convection begins once the dynamics resemble the Forchheimer regime of the reference simulations. Based on our data, the system is governed by the confinement parameter $\Lambda$, which relates the plume-neck width, equivalent to the thermal boundary-layer thickness, to the pore scale: for $\Lambda \gtrsim 1$, the dynamics follow Forchheimer scaling, while for $\Lambda < 1/2$ they shift toward Rayleigh--Bénard behaviour. Comparison with experimental data shows the same trend: the nominal $Ra^*/Pr_p \approx 1$ criterion holds for $\Lambda > 10$, but weaker confinement causes earlier departure. Finally, we revise benchmark Nusselt numbers for a cavity with square obstacles, showing that the reference by \citet{merrikh2005natural} misrepresents trends due to improper normalisation. (Paper accepted 2025-11-19)